Problems
Existence of a civilization obliged to burning of a hydrocarbon fuel.
As a physical-chemical phenomenon combustion is extremely complex process.
Canonical objects with clear boundary conditions are necessary to study of
chemical reacting. A boundary layer with burning of evaporating liquid fuel is among them.
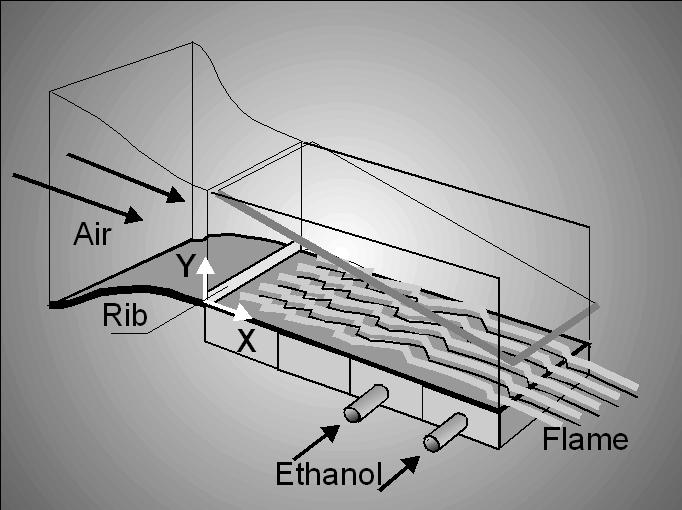
Fig.1. Scheme of the flow in the boundary layer with combustion behind a barrier.
Object of this study is characterized by several factors including transverse
substance flux on the wall, evaporation, combustion, acceleration and increased turbulence
of a incedent air flow.
Determination each of these values is necessary because it makes the process more
definite.
First, during adiabatic evaporation of ethanol (biofuel), the temperature on the wall and the gas and
vapor concentrations are preset and do not depend on the airflow velocity or its
turbulence.
Second, the presence of the barrier increases combustion stability, which is extremely
important for the investigation of the effects of various dynamic gas factors such as
acceleration and turbulence on the transfer process. Stability of combustion further aids
in the investigations under the conditions of increased airflow velocity, when the role
of natural convection and radiation heat transfer decreased.
Aforementioned specificity of the boundary layer is justified because it characterizes
the combustion process for natural conditions as well as for technical devices.
Some effects we found out during combustion
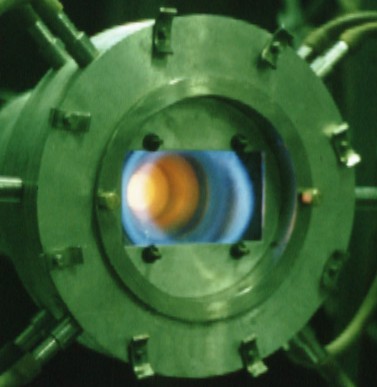
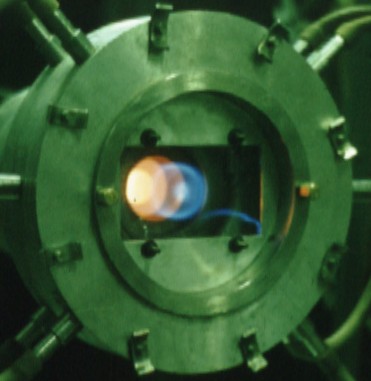
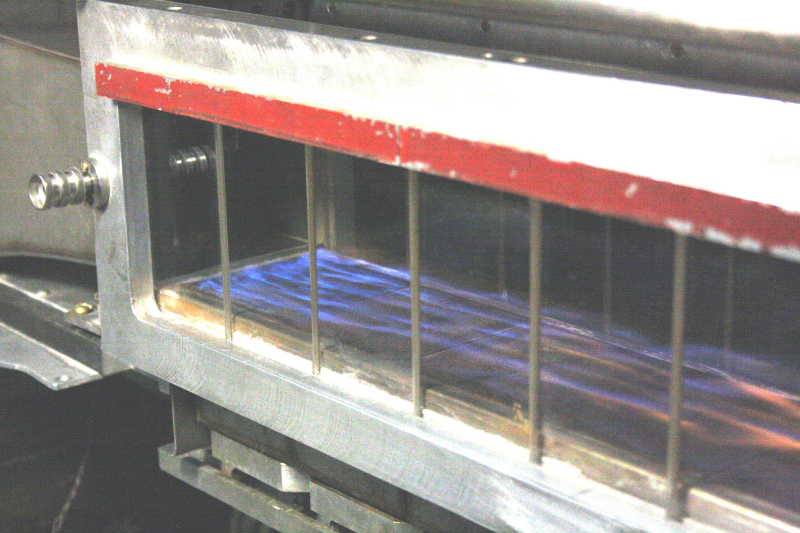
1. Replacement of combustion regions is one of them. The burning is absent near back
step before flame-out (left). After flame-out combustion takes place near back step only,
and disappears down the stream. Airflow is directed from left to right, step height
is 3 mm.


2. Coupling of transverse coherent structures is well-known process. The longitudinal
structures are formed behind a barrier. What are their properties? If the pictures
zoomed (click!), you can see a twist (left) and coupling (right) of longitudinal structures behind a back step.
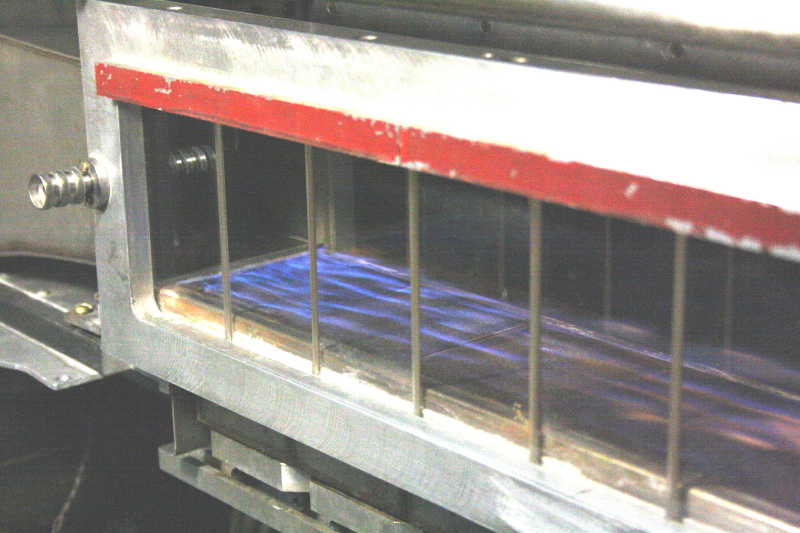

The time scale is the exposure duration of 1/400 s. The spatial scale is based on the
size of the quartz plates, which form the lateral walls. The plates are 65 mm in the
longitudinal direction, and the channel width is 100 mm.
3. "Hear pin" structures are on a vertical wall. They exist in a channel with falling
(left) and ascending (right) air current. Their number can change.


4. Cells during combustion of propane-air mixture are on the
stainless-still net (left - ascending flow). In a falling gas current (right) cells exist,
and the flame forms somewhat of a magic "burning flower".


5. Flame under control into vortex chamber.